The Colorado Ownership, Management and Protection (COMaP) spatial database is a project and product that was begun in 2004 at CSU by Dr. Dave Theobald. It has since gone through 9 versions with the publication of v9 in 2011. Versions 1-4 were funded by Colorado Parks & Wildlife (formerly the Colorado Division of Wildlife) as part of the Natural Diversity Information Source, versions 5-8 were funded by Great Outdoors Colorado (GOCO), and version 9 was funded by the USGS Gap Analysis Program as part of their goal to develop a Protected Areas Database of the United States (PAD-US). Future versions will be funded by user fees and donations. The seed money to develop the online mapping application was funded by GOCO and developed by GreenInfo Network.
The newest COMaP dataset has significantly updated federal and state lands (which make up almost half of the state) and an additional 355,000 acres of lands conserved under easements are now in COMaP compared to v9.
COMaP Versions:
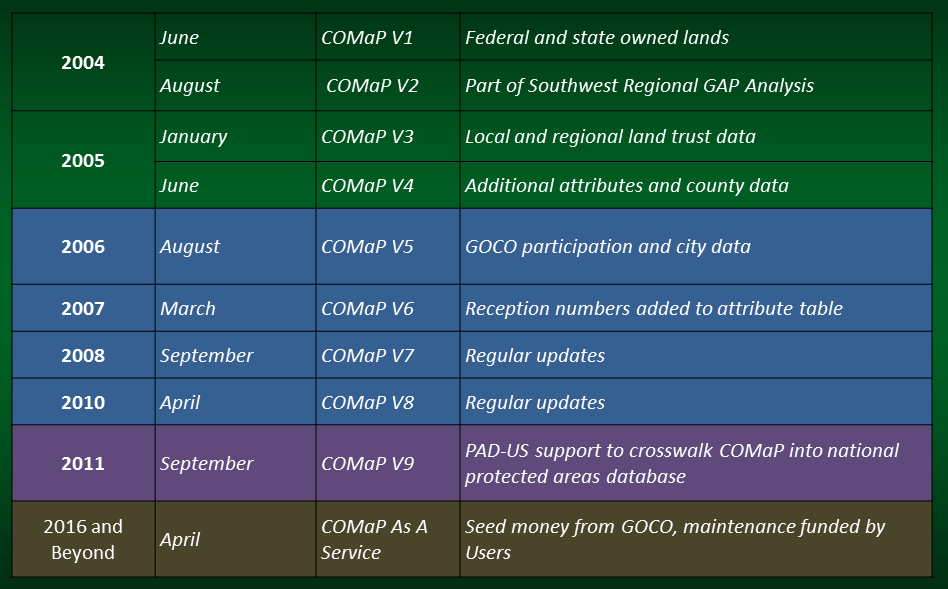
v1, 05/2004: This dataset identified all federal and state owned lands in Colorado. Given that COMaP is a synthesis of multiple datasets, there were numerous discrepancies in both the geometry and attributes. Feature level metadata was attributed to every feature in the dataset. In the event of a discrepancy, attributes were assigned to track the conflict.
v2, 08/2004: COMaP v2 was released as COMaP v2-SWReGAP. We coordinated with the South West Regional GAP (SWReGAP - http://swregap.nmsu.edu/) project to complete the stewardship layer for SWReGAP. The SWReGAP project study area encompasses five states: Colorado, New Mexico, Arizona, Nevada, and Utah. While the SWReGAP staff has focused on the other four states, COMaP was provided as the stewardship dataset for the Colorado portion of the project. In order for COMaP to mosaic with the other four states, attributes that tracked discrepancies were removed. This allowed for COMaP to fit with the other four states and complete the stewardship layer for SWReGAP analysis.
v3, 01/2005: By this version, the processing methods had evolved from the first two versions to produce a more consistent and “cleaner” dataset. The main difference is that we created a Python script to systematically assemble the original input datasets based on a ranking. The program identifies areas of overlap and exports them to a feature class. Manual editing was still necessary to address edge matching errors. Version 3 was developed in stages that allowed for two levels of the final output. This was done to allow for various levels of detail and to restrict access to sensitive information on private land conservation easements. COMaP_v3_public contained all federal and state data inputs as well as input from The Nature Conservancy. As county level data was reviewed and accepted, it was also incorporated into COMaP_v3_public. COMaP_v3_private went a step further to include inputs from local and regional land trusts. This final level, COMaP_v3_private, was released only to contributors that had a vested interest in private conservation easements.
v4, 06/2005: COMaP v4, released June 31, 2005, had additional attributes added to the database to create a clearer picture of land ownership, management and protection across the state. The new attributes include a detailed owner, a detailed manager, public access, protection mechanism, easement holder, date established, source scale, and a URL hotlink to the feature or feature manager web page. COMaP v4 also integrated all of the county data that had been acquired as well as datasets from two municipalities. COMaP v4 maintained the same public/private distinctions introduced in v3 as discussed above.
v5, 08/2006: For COMaP v5, the support from GOCO led us to create additional attributes in the database to better track GOCO’s participation in projects across the state. In this release of COMaP, attributes were added to the database to allow for better tracking of property and easement acquisition funding (FUNDING_PARTNERS, GOCO_FUNDING), additional details concerning protection processes and length (PROTECTION_TERM, PROTECTION_PROCESS), and an attribute to assist in open space analysis (GOCO_OS_TYPES). COMaP v5 also featured the addition of 24 city datasets, 12 county datasets, 14 land trust datasets, and a completely updated forest service boundary.
v6, 04/2007: COMaP v6 continued to build upon past data as well as adding more attributes to better track protections. Attributes added to v6 included, GOCO_LOG, ALT_GOCO_LOG, and RECEPTION_NO. We feel the reception number attribute will be a key component as we try to make sure all conservation easements across the state are included within the database and are accurately represented.
v7, 09/2008: COMaP v7 was completed by adding new easements from many land trusts and land exchanges, and better attributing of GOCO projects.
v8, 04/2010: COMaP v8 included updates from many of the agencies that had previously contributed to the dataset, as well as new data from agencies who had not contributed in the past.
v9, 09/2011: COMaP v9 included updates from many state and local agencies, land trusts and GOCO-funded easements. During version 9, stewardship of COMaP switched from Human Dimensions of Natural Resources and the Natural Resource Ecology Lab (NREL) to the Colorado Natural Heritage Program and the CSU Geospatial Centroid. Two attributes, ATTRIBUTE_DATA and ATTRIBUTE_DATE, were added to track parcels whose shapes were not replaced but had significant attribute changes (management codes, public access, etc.)
To view the list of specific data contributors, click HERE.






